


- 1 First Steps
- 1.4 Supported Host Operating Systems
- 1.8 Running Your Virtual Machine
- 1.10 Snapshots
- 1.14 Importing and Exporting Virtual Machines
- 1.15 Integrating with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- 1.18 Soft Keyboard
- 2 Installation Details
- 2.1 Installing on Windows Hosts
- 2.2 Installing on Mac OS X Hosts
- 2.3 Installing on Linux Hosts
- 2.4 Installing on Oracle Solaris Hosts
- 3 Configuring Virtual Machines
- 3.1 Supported Guest Operating Systems
- 3.2 Unattended Guest Installation
- 3.4 General Settings
- 3.5 System Settings
- 3.6 Display Settings
- 3.11 USB Support
- 3.14 Alternative Firmware (EFI)
- 4 Guest Additions
- 4.2 Installing and Maintaining Guest Additions
- 4.3 Shared Folders
- 4.4 Drag and Drop
- 4.5 Hardware-Accelerated Graphics
- 4.7 Guest Properties
- 4.8 Guest Control File Manager
- 4.10 Memory Overcommitment
- 4.11 Controlling Virtual Monitor Topology
- 5 Virtual Storage
- 5.11 vboximg-mount: A Utility for FUSE Mounting a Virtual Disk Image
- 6 Virtual Networking
- 6.3 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- 7 VBoxManage
- 7.8 VBoxManage modifyvm
- 7.10 VBoxManage import
- 7.11 VBoxManage export
- 7.37 VBoxManage unattended
- 7.38 VBoxManage snapshot
- 7.39 VBoxManage clonevm
- 7.40 VBoxManage sharedfolder
- 7.41 VBoxManage extpack
- 7.42 VBoxManage dhcpserver
- 7.43 VBoxManage debugvm
- 7.44 VBoxManage cloudprofile
- 7.45 VBoxManage cloud
- 7.46 VBoxManage signova
- 7.47 VBoxManage updatecheck
- 7.48 vboximg-mount
- 1 First Steps
- 1.4 Supported Host Operating Systems
- 1.8 Running Your Virtual Machine
- 1.10 Snapshots
- 1.14 Importing and Exporting Virtual Machines
- 1.15 Integrating with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- 1.18 Soft Keyboard
- 2 Installation Details
- 2.1 Installing on Windows Hosts
- 2.2 Installing on Mac OS X Hosts
- 2.3 Installing on Linux Hosts
- 2.4 Installing on Oracle Solaris Hosts
- 3 Configuring Virtual Machines
- 3.1 Supported Guest Operating Systems
- 3.2 Unattended Guest Installation
- 3.4 General Settings
- 3.5 System Settings
- 3.6 Display Settings
- 3.11 USB Support
- 3.14 Alternative Firmware (EFI)
- 4 Guest Additions
- 4.2 Installing and Maintaining Guest Additions
- 4.3 Shared Folders
- 4.4 Drag and Drop
- 4.5 Hardware-Accelerated Graphics
- 4.7 Guest Properties
- 4.8 Guest Control File Manager
- 4.10 Memory Overcommitment
- 4.11 Controlling Virtual Monitor Topology
- 5 Virtual Storage
- 5.11 vboximg-mount: A Utility for FUSE Mounting a Virtual Disk Image
- 6 Virtual Networking
- 6.3 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- 7 VBoxManage
- 7.8 VBoxManage modifyvm
- 7.10 VBoxManage import
- 7.11 VBoxManage export
- 7.37 VBoxManage unattended
- 7.38 VBoxManage snapshot
- 7.39 VBoxManage clonevm
- 7.40 VBoxManage sharedfolder
- 7.41 VBoxManage extpack
- 7.42 VBoxManage dhcpserver
- 7.43 VBoxManage debugvm
- 7.44 VBoxManage cloudprofile
- 7.45 VBoxManage cloud
- 7.46 VBoxManage signova
- 7.47 VBoxManage updatecheck
- 7.48 vboximg-mount
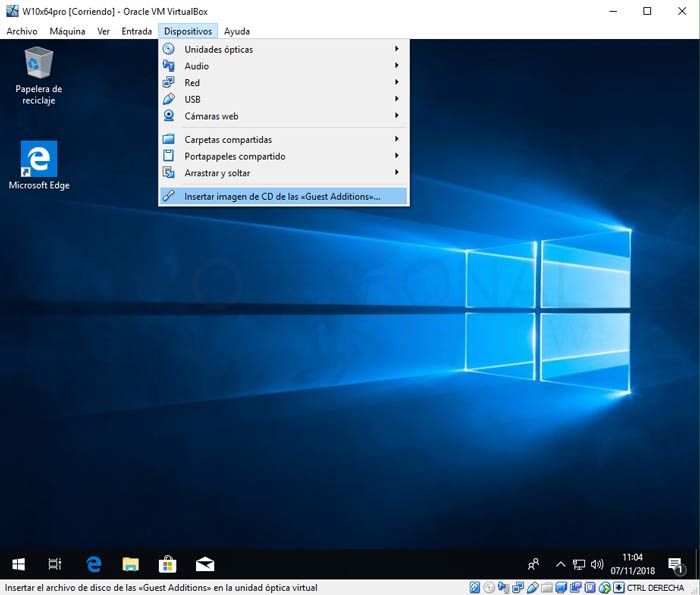
Install Guest Tool on macOS 10.15 Catalina on VirtualBox. Most you might not be familiar with the Guest tool, but you may familiar with installing VMware tool on macOS Catalina. The process on how to install it on VMware and VirtualBox are the same. To do this follow each of the steps instructions. Professor Robert McMillen shows you how to install Guest Additions in VirtualBox.
Mac Os Guest Additions Virtualbox
Introduction to Guest Additions. As mentioned in Section 1.2, 'Some Terminology', the Guest. The Guest Additions for anything ≥10.14 need to be notarized in order to be allowed to install the kexts. Currently they're not. It doesn't have anything to do with the read-only filesystem in 10.15. And BTW, you have a 10.14 guest, that doesn't even come into play.
